In this article, we will see how to deploy laravel on heroku with database. Heroku is a cloud platform as a service (PaaS) supporting several programming languages. Developers use heroku to deploy, manage, and scale modern apps. heroku platform is elegant, flexible, and easy to use, offering developers the simplest path to getting their apps to market. Heroku offers a free plan to help you learn and get started on the platform. Heroku Buttons and Buildpacks are free, and many Heroku Add-ons also offer a free plan.
So, let's see how to deploy laravel with the database on heroku, deploy laravel to heroku with the PostgreSQL database and deploy laravel to heroku from GitHub.
Here, we will show you how to host the laravel project on heroku or deploy laravel to heroku with the database. here we will use the PostgreSQL database.
Step 1: Install/download Heroku CLI
Step 2: Install Laravel Application
Step 3: Create a proc file
Step 4: Initialize git repo
Step 5: Login into the Heroku and create App
Step 6: Push Laravel changes to Heroku
Step 7: Configure the postgresql Database on Heroku
Step 8: Add the project files and run the migration
First of all, you need to download or install Hiroku CLI as per your operating system, here I have a window so I have download Hiroku-x64.exe from the official website.
You can also download it from here: Download Heroku CLI
This installation method is required for users on ARM and BSD. You must have node and npm installed already.
npm install -g herokuNow, we need to check and verify whether heroku is installed or not. So, copy the below command in your terminal.
heroku --versionIn this step, we will install laravel using the following command.
composer create-project laravel/laravel Laravel_8_Auth --prefer-distInside the Laravel main folder create a file and set the name Procfile. add the following line inside the Procfile.
web: vendor/bin/heroku-php-apache2 public/ 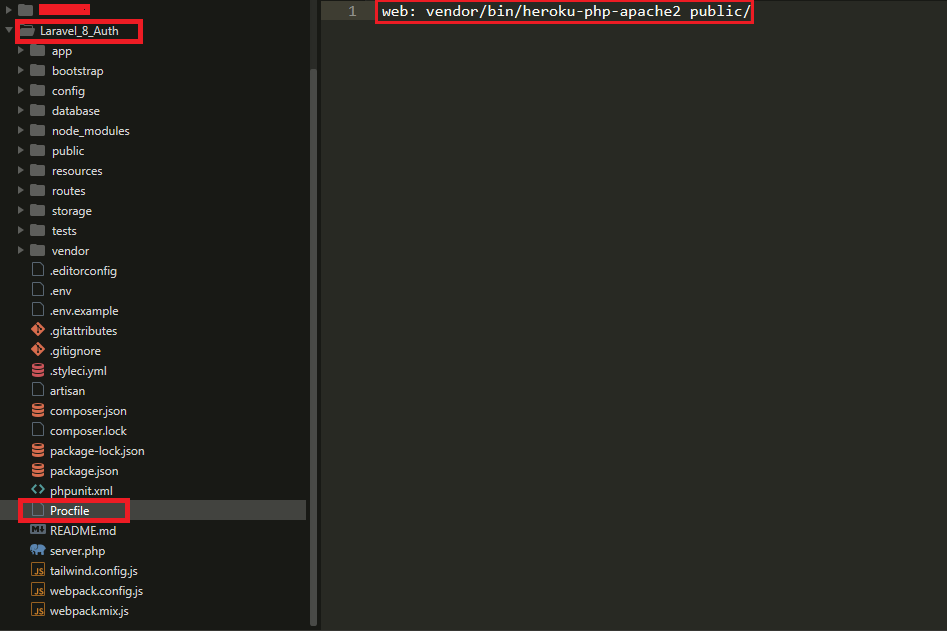
Initialize the Git repository using the below command.
git initNow, login into heroku app using the web and create a new app file. here I have created a new app with the name laravel-8-auth

Now, add the below code for adding files on git commit and push changes as below.
git add .
git commit -m "laravel 8 auth heroku"
$ git push heroku masterwe have used Postgres Database because it is free on Heroku. So we need to use an add-on database provision provided by Heroku. You can find more PostgreSQL.
Type the following command to create a PGSQL database.
heroku addons:create heroku-postgresql:hobby-devNow, we need to config the database on heroku.
heroku configafter that, we will find 2 values as below.
- APP_KEY
- DATABASE_URL
Now, copy the DATABASE_URL and open your config >> database.php file.
First, change the default database to pgsql from MySQL.
Now, at the top, you need to define $DATABASE_URL = parse_url(“Your generated database URL, copy here”).

$DATABASE_URL=parse_url('Your database URL');Now, your pgsql database config array looks like this.
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Str;
$DATABASE_URL=parse_url('your database URL key');
return [
'default' => env('DB_CONNECTION', 'pgsql'),
'connections' => [
'sqlite' => [
'driver' => 'sqlite',
'url' => env('DATABASE_URL'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE', database_path('database.sqlite')),
'prefix' => '',
'foreign_key_constraints' => env('DB_FOREIGN_KEYS', true),
],
'mysql' => [
'driver' => 'mysql',
'url' => env('DATABASE_URL'),
'host' => env('DB_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'port' => env('DB_PORT', '3306'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE', 'forge'),
'username' => env('DB_USERNAME', 'forge'),
'password' => env('DB_PASSWORD', ''),
'unix_socket' => env('DB_SOCKET', ''),
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
'collation' => 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci',
'prefix' => '',
'prefix_indexes' => true,
'strict' => true,
'engine' => null,
'options' => extension_loaded('pdo_mysql') ? array_filter([
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_SSL_CA => env('MYSQL_ATTR_SSL_CA'),
]) : [],
],
'pgsql' => [
'driver' => 'pgsql',
'url' => env('DATABASE_URL'),
'host' => env('DB_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'port' => env('DB_PORT', '5432'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE', 'laravel_8_auth'),
'username' => env('DB_USERNAME', 'root'),
'password' => env('DB_PASSWORD', ''),
'charset' => 'utf8',
'prefix' => '',
'prefix_indexes' => true,
'schema' => 'public',
'sslmode' => 'prefer',
],
'sqlsrv' => [
'driver' => 'sqlsrv',
'url' => env('DATABASE_URL'),
'host' => env('DB_HOST', 'localhost'),
'port' => env('DB_PORT', '1433'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE', 'forge'),
'username' => env('DB_USERNAME', 'forge'),
'password' => env('DB_PASSWORD', ''),
'charset' => 'utf8',
'prefix' => '',
'prefix_indexes' => true,
],
],
'migrations' => 'migrations',
'redis' => [
'client' => env('REDIS_CLIENT', 'phpredis'),
'options' => [
'cluster' => env('REDIS_CLUSTER', 'redis'),
'prefix' => env('REDIS_PREFIX', Str::slug(env('APP_NAME', 'laravel'), '_').'_database_'),
],
'default' => [
'url' => env('REDIS_URL'),
'host' => env('REDIS_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'password' => env('REDIS_PASSWORD', null),
'port' => env('REDIS_PORT', '6379'),
'database' => env('REDIS_DB', '0'),
],
'cache' => [
'url' => env('REDIS_URL'),
'host' => env('REDIS_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'password' => env('REDIS_PASSWORD', null),
'port' => env('REDIS_PORT', '6379'),
'database' => env('REDIS_CACHE_DB', '1'),
],
],
];
Now, add the file to the heroku and run the below command.
git add .
git commit -m "laravel 8 auth heroku"
$ git push heroku masterRun migration.
heroku run php artisan migratenow, enter yes if ask and you will be able to create the tables in the database.
Output:

You might also like:
- Read Also: Laravel 8 Toastr Notifications Example
- Read Also: Node.js Express CRUD Example with MySQL
- Read Also: Bootstrap Session Timeout Example In Laravel
- Read Also: How to Set Auto Database BackUp using Cron Scheduler In Laravel