Java is a well-established and widely-used programming language. You can use it to create desktop and mobile applications, for massive data processing, for backend development, to program embedded devices, and more.
Oracle, the company that owns Java, claims that Java is used on 3 billion devices worldwide, making it one of the most popular programming languages.
In this article, we will discuss the history of Java, reasons to use Java for backend development, the top tech companies that already use Java for this purpose, and the top Java frameworks for backend development.
We will also explore the benefits and drawbacks of using Java for backend development.
History of the Java Programming Language
Java was launched in 1991 when James Gosling and his team at Sun Microsystems began development on the language.
Soon after, the team shifted its focus to developing the language for the newest specialized market, the World Wide Web.
Java was offered to the public in 1995 for usage in various applications ranging from the internet to computer programming. According to learncodewith.me, Java is one of the top three programming languages in the world for backend development. It's also ranked first among the top ten programming languages for 2022.
Why You Should Use Java for Backend Infrastructure
The following are some benefits of using the Java programming language for backend development.
Scalability and Robustness
Java has a robust type-checking mechanism that makes it durable. The Java virtual machine (JVM) enables dynamic linking and a secure environment, allowing Java to run anywhere.
Java's automatic memory management and disposal collection make it highly scalable and these features help speed up web application development.
Open Source Library
The vast majority of Java libraries are free and open-source, with expert support. The use of such libraries speeds up the back-end programming of web projects dramatically.
There are many Java libraries for various uses, including logging, JSON parsing, unit testing, XML and HTML parsing, messaging, PDF and Excel reading, cryptography, and many others.
Diversity
Java has long been the dominant programming language for developing Web applications, Android applications, and software tools such as Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, NetBeans IDE, and others.
Java's use cases have now grown to include data science applications, machine learning applications, and even IoT applications.
Simplicity
Java syntax is relatively simple, easy to develop, learn, maintain, and understand, and the code is easily debuggable.
Java is also less complex than languages such as C and C++ because many of these languages' sophisticated features, such as explicit pointers, storage classes, operator overloading, and many others, have been eliminated from Java.
Security
Java reduces security concerns and dangers by reducing the use of explicit pointers. A pointer is a value that keeps the memory address of another value and can be exploited to gain unwanted memory access. This issue is solved by removing the concept of pointers.
Platform Independency
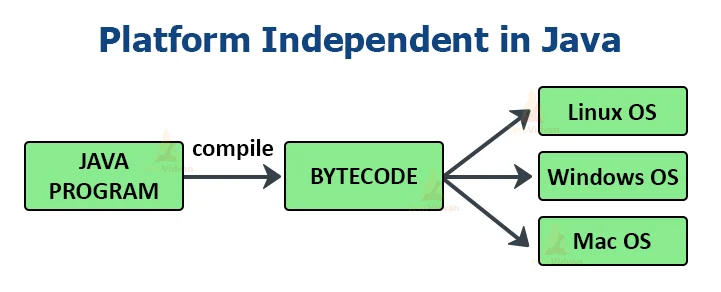
Java is platform-independent, which means it's a "Write Once, Run Anywhere" (WORA) language.
The compiled code (the byte code of Java) is platform-independent and can run on any machine, irrespective of the operating system. We can run this code on any machine that supports the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), as shown in the figure above.
Multithreading Support
Java is a multithreaded language, which means that multiple threads can run at the same time.
A thread is a process's smallest unit. Multithreading allows us to maximize CPU use. Multiple threads share the same memory space, increasing the application's efficiency and performance.
Drawbacks of the Java Programming Language
Lack of Backup Facility
Java is primarily concerned with storage and does not prioritize data backup. This is a huge drawback, and it is losing user interest and ratings as a result.
Code Complexity
Java code is extensive, which means it contains many words and long, complex sentences that are hard to read and comprehend. This reduces the code's readability.
Java strives to be more manageable, but it must settle for unnecessarily complex programs and detailed explanations for each thing.
Speed and Performance Level
Java consumes a large amount of memory and is substantially slower than native languages such as C or C++. This is partly because each bit of code must be interpreted into machine-level code. This slow performance is caused by the JVM's additional level of compilation and abstraction.
Memory Capacity
When compared to other languages such as C and C++, Java uses a significant amount of memory. Memory efficiency and system performance may suffer during cleanup execution.
Top Companies That Use Java
To begin with the list, according to statistics based on Codegym, 10,130 companies are said to employ Java in their IT stacks. Not unexpectedly, the United States leads among enterprises that use Java, accounting for more than 60% of Java clients (about 64,000 businesses).
Linkedin: This application is primarily written in Java, with some C++ parts thrown in for good measure. Java is excellent for LinkedIn's search and analytics. More specifically, it addresses scale concerns, allowing the server to function faster while using fewer resources.
Uber: Uber is the next big Java-based firm. The organization works with a large amount of real-time data, tracking drivers and incoming ride requests. As a result, Uber should be able to sift the data and match users swiftly. That's where Java comes in, handling requests and transmitting data as quickly as possible.
Microsoft: Even though Java does not control Windows or anything similar, Microsoft uses it for various purposes. For example, it requires Java to construct its proprietary Edge web browser.
NASA World Wind: NASA built the Word Wind app, which features a realistic 3D virtual globe and can display precise geographical data, largely thanks to Java (the program uses actual images from satellites to develop 3D representations of the planets). It's an open-source program that runs on practically any operating system because it's developed in Java.
Netflix: Netflix, the same as PayPal, primarily uses Java for practically everything. And because Netflix is one of the best-known entertainment platforms in the world, there is a significant demand for Java expertise in this organization.
In addition to the tech titans mentioned earlier, Java is used by Airbnb, Google, eBay, Spotify, TripAdvisor, Intel, Pinterest, Groupon, Slack, Flipkart, and many more. Without a doubt, you can find Java practically anywhere.
Differences Between a Java Backend and a Node.js Backend
Java and Node.js are both popular choices for building server-side applications. But they have some key differences that make each one better suited for different use cases.
In terms of strengths, Java has the advantage of being a statically-typed language, which provides better performance and stability. Java also provides better security features, such as the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which has memory protection and isolation. Java also has a large number of libraries and tools available, which makes it easier to develop and maintain large-scale applications.
Node.js, on the other hand, has the advantage of being a dynamically-typed language, which makes it easier to learn and more flexible. Node.js is also well-suited for real-time applications, such as chat applications, thanks to its event-driven architecture. Node.js also has a large and active community, which provides a wealth of libraries and tools for various tasks.
In terms of weaknesses, Java can be slower to develop and more complex compared to Node.js, due to its strong typing and verbose syntax. Java also requires more memory compared to Node.js, which can make it less suitable for low-memory devices.
Node.js, on the other hand, has weaker type checking compared to Java, which can lead to unexpected errors. Node.js also has a single-threaded architecture, which means that it is not as well-suited for multi-threaded applications compared to Java.
In conclusion, both Java and Node.js have their own strengths and weaknesses for backend development. Java is well-suited for large-scale and complex applications, while Node.js is well-suited for real-time and scalable applications. The choice between the two ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the project.
Top Java Frameworks for Backend Development
There are various Java backend frameworks, each with its own capabilities and features. Below are a few popular examples:
Spring
The Spring framework is a lightweight Java application framework and an inversion of a control container.
The framework's core functionality can be used by any Java application, although there are enhancements for constructing web applications on top of the Java EE framework.
Hibernate
Hibernate ORM is an object-relational mapping tool written in Java that provides a framework for translating a relational database into an object-oriented domain model.
Play
The Play Framework combines productivity and performance, making it simple to create scalable Java and Scala online applications. Play is developer-friendly, with a "simply hit refresh" workflow and testing support built in.
Because of Play's stateless and non-blocking architecture, applications scale reliably. Play is ideal for current online and mobile apps because it is RESTful by default and includes asset compilers, JSON, and WebSocket support.
Struts
Apache Struts is a free and open-source web application framework used to create Java EE web applications. It uses and improves the Java Servlet API to encourage developers to use a model-view-controller paradigm. Craig McClanahan designed it and presented it to the Apache Nation.
Conclusion
In this article, you learned about the Java programming language's history. You have also learned the key distinctions between Java and Node.js, clearing up any uncertainty.
Finally, you understand what Java is used for, the industries in which it can be found, and some of its distinguishing traits. You can now use it in your own web apps for seamless backend development.