B. Attacker
I. what is the attacker? Who are the attackers?
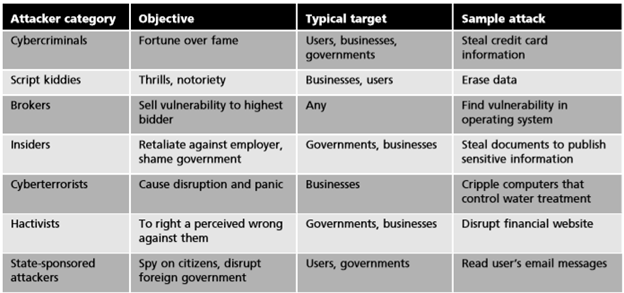
The word "hacker" sounds a bit strange, previously known as "hacker". The word "hacker" does not really mean anything, it's just a word for people who know and understand the system and how they work. Black hat attackers are attackers who violate computer security for personal gain (such as stealing credit card numbers) or damaging the hard drive. White hat hackers are described as "moral attackers": with the permission of the organization, they will try to probe a system for any weaknesses and then provide information to the organization. Of any undetected vulnerabilities. In the middle are hackers who will try to break into a computer system without the permission of the organization (an operation) but not for their own advantage; Instead, it will publicly disclose the vulnerability to cause embarrassment to the organization taking action. But current it is split out to many attack types, that is Cybercriminals, Script Kiddies, Brokers, ... The following table details each attacker:
There are 7 steps of an attack:
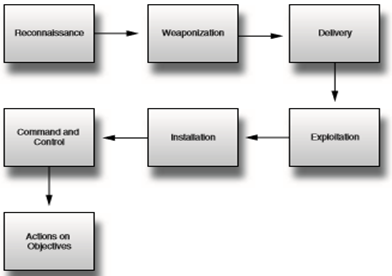
Step 1: Reconnaissance. Is the first step of an attack. The attacker must seek information about the system or the manager, to assess and plan the perfect attack.
Step 2: Weaponization. An attacker who creates weapons (such as worms with viruses) optimally can attack the rock system, and then encapsulate it to be able to infiltrate the system, accomplishing their purpose.
Step 3: Delivery. This is a move from the attacker to the system via mail, or a package.
Step 4: Exploitation. When the weapon arrives, they begin to be activated and used to serve the attacker's purpose.
Step 5: Installation. The weapon was moved to the place and then to the installation step. When installed on, an attacker could gain access, destroy the system or victim machine remotely.
Step 6: Command and control. Attackers start executing code or controlling their weapons for their conspiracy.
Step 7: Actions on objectives. Is the last step of an attack. Attackers begin to perform their initial purposes.
II. How to defense
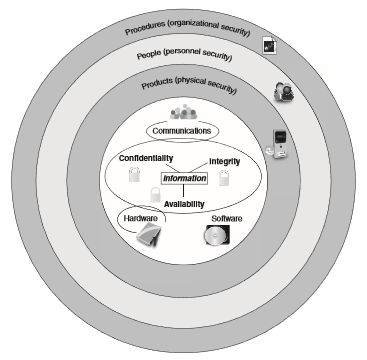
has 5 basic security raw: layering, limiting, diversity, obscurity, and simplicity. Layering: Your simplicity may be just in order for your ironing to be safe, for many more keys will be possible.
Limiting: You can understand in other words the terms. Only the permission of the right of the user's right of the maximum level.
Diversity: This rule is available with primary partition. There are many types of layers and should be many. Like the example in the resource class, multiple locks must be of different types, it can not be very basic at the attack.
Obscurity: You can understand simple code later. You also know first in an attack is a compiler. But when at least known, the compiler will also collect small information. And to do so, crooks can not access an easy information.
Simplicity: With the partitioning example of the database, if you have multiple locks, fine but if you can solve the problem for the user, they may also not be allowed to access, but not be hacked, do As such, simplification can be used for the user to be able to use and protect your information.
Moreover, a normal information protection will be broken down as shown below like many layers protect information:
III. Some types of malware
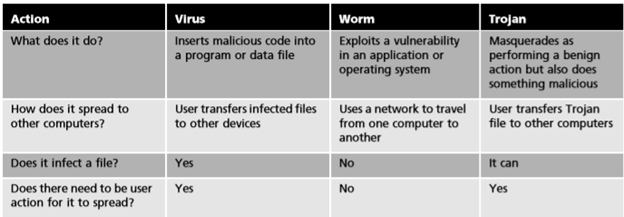
Three types of malware have the primary traits of circulation and/or infection. These are viruses, worms, and Trojans.
1. Viruses
Computer virus, you can simply understand it is a software program capable of copying itself from one infected object to another (the object may be program files, text, calculation ...). Viruses are more infectious and more destructive, but you simply understand it as a code or program and they are used to serve the purpose of the person who created it. Most of all, it's a bad thing.
Computer viruses are man-made, so far, we still have to fight with these viruses. It's like a virus, in fact, every time there is a way to prevent the old virus, the new one is born. So we still have to fight for them in the long run.
For example, These is Sasser and Netsky – dangerous viruses A 17-year-old German named Sven Jaschan created the two viruses and launched them on the Internet. Although there are different ways of doing things, the similarities in code have led experts to believe that this is the "work" of the same person. Sasser attacked the Microsoft Windows vulnerability but did not spread through email, instead searching for other vulnerable systems. It will connect these systems together and guide them to download the virus. The virus will scan the IP addresses at random to find out the victims. The computer will not turn off if the power is not cut off. Netsky virus spread through email and Windows network, causing network congestion.
2. Worms
Worm, you can understand it is a software program that has the ability to independently copy itself to spread to other computers. Typically, a worm uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security vulnerabilities on the operating systems installed on the target computer for access and spread. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to manually attach to a program that is activated. This is the type of malicious code considered to be the most dangerous because they are likely to burst into danger for computer networks due to the ability to spread very quickly.
Worms almost always cause harm to the computer network, even though it only consumes bandwidth leading to slowing down the network, and can lead to network congestion. Here is an example of a worm that has been threatening many computers: "Deep" Morris (1988). This has made many computers slow down the network connection, resulting in not too big but not too small as it could be the beginning of attacks using other worms. However, it does bring a lot of enthusiasm to later people, just having an idea and determination, you can do many things that you think are just fictional. In 1988, a normal college student came up with the idea of measuring the size of the Internet. To do that, he created a worm to infiltrate the Internet and connect to computers using the network. However, the Morris Worm can be infected multiple times on the same computer and slow down their speed. As a result, up to 10% of the computers connected to the Internet at that time (an estimated 60,000) were affected by the Morris Worm and slowed down or even stopped. As for Morris, he is now a professor at MIT, USA.
3. Trojan
Trojans are defined as trojans with the legendary Trojan horse. It will be malicious code attached to the program, or link, or utility application for the victim.
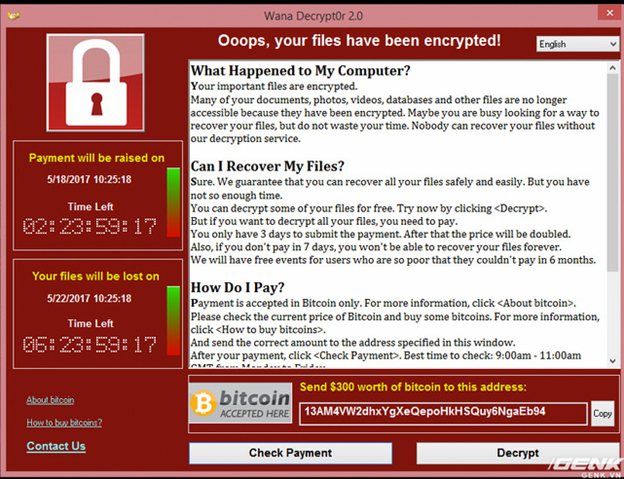
Such as WannaCry. Have you ever heard from WannaCry. It is a worm attack. In May 2017, a large-scale cyberattack using it was launched, as of May 15 (3 days after it was known), which infected more than 230,000 computers in 150 countries. , requesting payment of a ransom of 300 to 600 euros in bitcoin in 20 languages (including Thai and Chinese). Currently, there are 5 accounts of their bitcoin, so far no more than 130 people pay, the maximum income is only about 30,000 Euros. This attack has affected Telefónica and a number of other large companies. in Spain, as well as parts of the British National Health Service (NHS), FedEx and Deutsche Bahn. Other targets in at least 99 countries have also been reported to have been attacked at the same time. More than 1,000 computers in Russia's Ministry of Internal Affairs, the Russian Ministry of Emergency and the Russian telecommunications company MegaFon have reportedly been infected.
The following table shows the differences between viruses, worms and trojans
4. Ransomware.
Ransomware - You must have heard this name many times already. Ransomware, spyware, blackmail software are all 1. This is the generic name of a form of malware - Malware, the "effect" is to prevent users from accessing and using the system. Their computer system (mainly detected on the Windows operating system). Malware variants often send messages to victims that they have to pay a decent amount of money to the hacker's account if they want to retrieve their data, personal information or simply access the machine. their temperament. Most Ransomware software takes over and encrypts all of the victim's information it finds (often called Crypto locker, while some other Ransomware use TOR to hide and hide C & C packets. computer (another name is CTB Locker).
The price that Ransomware offers to victims is also varied, "light" is $ 20, "heavyweights" can be up to thousands of dollars (but on average $ 500 - 600), there are also case of accepting payment by Bitcoin.
However, you need to pay attention that even if you pay for the hacker, the percentage of users who get back the data, personal information is not 100%.
Like other malware, Ransomware can infiltrate a user's computer when: • Finding and using cracking software, • Clicking on ads, • Accessing black web pages, • Deceiving websites • Accessing fake websites Download and install non-originating software, email attachments,.etc. For the first time, Ransomware was discovered between 2005 and 2006 in Russia. The first TrendMicro reports were in 2006, with the variant TROJ_CRYZIP.A - a form of Trojan that enters a user's computer, instantly encrypts, compresses system files with password, Time to create the * .txt files with content that requires victims to pay $ 300 to get back personal data.Still developed over time, the Ransomware attack to the next file system and text as * .DOC, * .XL, * .DLL, * .EXE ...
And by 2011, another form of Ransomware was SMS Ransomware. The way Ransomware SMS differs slightly, is that the user must send a message or call the phone number of the hacker, until the transfer procedures for the hacker. This variant of Ransomware was discovered under the name TROJ_RANSOM.QOWA - will continuously display fake notifications on the computer screen. In addition, there is another variant of Ransomware - much more dangerous with the hacker's goal of attacking the Master Boot Record (MBR) of the operating system. And when hacked, the operating system - Windows will not be able to boot. More specifically, these Malware will copy the original MBR of the system and overwrite it with a fake MBR. When complete, this process will restart the computer, and the next time the hacker's message (in Russian) will be displayed on your screen.The above are three variants of Ransomware and their attacks.
In addition, on March 22, officials from the city of Atlanta, Georgia, in the United States said the city's computer system had been hacked by malicious hackers. ransomware). This attack has caused many of the city's applications, including in-house applications, to stop working, including billing software and access to court-related information. The hacker has asked the city government to pay a $ 51,000 ransom in Bitcoin to get back control of the files.
On May 12, more than 75,000 cyberattacks were reported in nearly 100 countries around the world, of which the UK suffered the most.
According to Kaspersky Lab's computer security technology company, they have recorded 75,000 cyberattacks in nearly 100 countries. In addition to the UK, other heavily affected countries are Russia, Spain, Ukraine and India. Spain's giant telecoms giant, Telefonica and FedEx Corp., are among the victims of the attack. The British public health sector is under attack and most affected, causing chaos in hospitals in the island of fog. Surgical cancellations, emergency ambulances were suspended and patients could not be hospitalized because the computer systems of more than 40 hospitals of the NHS were affected, leaving the team Doctors can not access medical records.
Previously, the attack on Sony Pictures Entertainment in 2014 cost an estimated $ 15 million to settle a lawsuit from the user, with about 77 million affected accounts restored.
5. how to spread Ransomware
According to information from the network and the press, there are now two ways to spread Ransomware in general.
a. Way 1
Spread it through the usual way is to embed the crack 's software and then share it online, embedded in the site has many visitors (porn sites, pirated software - non - copyright). The purpose is to trick users into downloading and enabling, or visiting bad sites then sticking.
b. Way 2 WannaCry, in particular, is spreading because it is not just spreading the traditional way, but also spreading across the LAN by utilizing the SMB exploit tools developed by the NSA (National Security Agency). secret, but was later stolen by the ShadowBroker team and released publicly from last month. When Shadow Broker launches these tools, security experts have predicted a mass exploit like WannaCry is doing. If a machine on a LAN is infected with WannaCry, all the machines in the network can be infected. If not patched before. c. Anti-Ransomware, especially WannaCry
- Latest Windows patch update: Microsoft is currently updating to Windows to fix SMBv1 security issues to avoid spreading. You should enable the Windows Update feature to get this update. However, Windows XP can not turn off SMB so it can only update security patches.
- Disable SMB features: Go to Start> type Windows Features> then uncheck SMB 1.0 / CIFS File Sharing Support.
- Update the antivirus: Currently, Windows Defender, McAfee, Symantec, ESET, Bitdefender ... have updated the ransomware WannaCry. After updating AV, you turn on Realtime Protection protection to prevent your computer from being infected.
- Data backup is the only way to block the damage from WannaCry and the ransomware. You should backup (backup) regularly. For personal users, it's a good idea to use a portable hard drive, copy the important data to a hard drive, and then remove it. Do not plug in frequently, need to plug in backup or retrieve data.
- Use Cloud Drive services like Google Drive, OneDrive, DropBox to regularly sync your data to Cloud. The price of these services is cheap, Google Drive free 15GB, and sell 100 GB with 45,000 VND a month, or 250,000 for 1000 GB (1TB). Or buy Google Enterprise for $ 15 a month with unlimited storage.
d. What should we do when the machine is infected with Ransomware When the machine is infected with Ransomware, these are the ways in which the damage is minimized.
- You need to immediately shut down the infected computer from the LAN so that it will not spread through other machines.
- Pay the author of WannaCry to receive the encrypted file decryption code is your decision. There are currently only 160 transactions worth about $ 300,000 sent to the BitCoin address the hacker has provided. Officially, WannaCry requires 2 BitCoin equivalent to 80 million, a rather sour number.
- There is information that WannaCry has an error in the way data is encrypted, so security experts are trying to find a way to exploit and write decryption tools. If the data is too important then the hard disk can be left waiting for the tool to be provided.
- If there is nothing to lose, then you can reformat the entire hard drive and reinstall Windows, it is possible that this ransomware is installed in many places so it is necessary to format the whole hard drive.
In the last year, while facing WannaCry, it was reported that another type of Ransomware was prepared for global threat. That is EternalBlue. At the moment, it does not pose any danger, but it has vulnerabilities that the crooks can use to attack. It's even more advanced and advanced than WannaCry. Today, the risk of WannaCry has been prevented. But EternalBlue is still vacant. I think EternalBlue or WannaCry is a variant of Ransomware. So Ransomware is never completely blocked, because every protection, every layer of protection can still be exploited. So now maneuvers or layers of protection are routinely checked by multiple levels of staff.
IV. Security hole Zeroday
1. What is the security vulnerability Zeroday?
The zero-day vulnerability is a term for unpublished or unresolved vulnerabilities. Taking advantage of these vulnerabilities, hackers and criminals can infiltrate the computer systems of corporations and corporations to steal or change data. Zero-day vulnerabilities in the Internet.
The average life span of a zero-day vulnerability is 348 days before it is discovered or patched, with many more vulnerabilities still alive. Cybercriminals are willing to pay huge amounts of money to buy zero-day vulnerabilities.
The "Zero Day" attack, according to Burleson Consulting, is defined as an attack that takes place in a short time, usually less than a day (hence the term "zero-day"). Zero-day attacks are carefully directed to maximize damage in a day because traditional anti-virus tools (patch software) do not have enough time to react.
For example, Assume I'm the only maintainer of the premium WordPress plugin with a small user base, and recently I've deployed an update that includes a bug for all my plugin users. In this example, I do not have code auditors like other developers, this is really bad and makes the vulnerability not detected by manual or automated tests. To complement this bad script, none of my plugin users have enough interest to test the new code. So, this vulnerability is just there, unnoticed.
Is this the Zero-Day flaw? Yes, it was the Zero-Day flaw.
If an attacker learns about the vulnerability, it will not change anything because the attacker will not care to patch it; However, they will be interested in exploiting it.
2. Why is the vulnerability of Zero-day so important?
Attackers love the Zero-Day vulnerabilities because there are no security patches to block them, and the only thing limiting them is the level of exploitation that the vulnerability allows. Some vulnerabilities require a certain amount of privilege to be exploited - but again, this depends on the vulnerability.
The hacker is actually taking the initiative to test whether a website has a vulnerability through the use of specific attack vectors. If this is not enough, hackers also use automation because it allows them to scan the Internet to find sites that match specific vulnerabilities and vulnerabilities.
A Zero-day attack can affect your online presence in different ways. These effects include lost revenue, compliance violations, wasted time, and damage to your brand's reputation.
Zero-Day attacks depend on a number of important factors:
- The security of the person who maintains the project.
- The quick response of the project maintainer if a problem occurs.
- Active security for the community using the project (CMS, plugin, etc.).
- The rapid response of the community to use the project if something goes wrong.
- Repetition is intentional. Both developers and site owners should actively protect their site and may respond quickly in the event of a problem. This means tracking down the signs of a problem and taking measures to prevent zero-day exploits if there is no security patch for the vulnerability.
If interested parties - developers and users - do not meet the security challenges of the website proactively, the only thing left to assess the impact of the Zero-Day vulnerability is to Know the number of systems affected. Automation makes it easy for hackers to use Zero-Day vulnerabilities.
The following reason making the popular Zeroday that are:
- It is not detected by the classic virus
- It easily input into the computer through the holes not been detected
- It can be used with the following code after being released.
3. how to protect from Zeroday.
Developers need to have processes to avoid vulnerabilities. These processes may include:
- Auditor code
- Bug bounty program
- Manual check
- Automated testing
- Security Alert There are some questions when you are creating a piece of software and check yourself for a zeroday vulnerability:
- Do I have a security solution in place that will help me mitigate the risk until there are fixes?
- Do I have a plan in case my software is compromised?
If the answer to the questions is not, then you should pray that these hackers will not find holes in your software.
In my opinion, best way to prevent Zeroday hole(how the users at the professional or even could not know any information about security information) :
- Always update patches and upgrades to your operating system and whatever software you are using. The new vulnerabilities discovered will fix in these updates.
![image.png]()
- Use anti-virus software with behavioral protection technology. Behavior-based protection is a technology used to detect new viruses based on tracking their behavior. When the virus infects the computer. The antivirus software will monitor and analyze its subsequent behavior. If the virus performs abnormal and suspicious behaviors such as logging operations on the keyboard, downloading logins, encrypting ransomware, trying to change the host file or extract the malicious code, etc. Once detected abnormal behavior, the antivirus software will quarantine and stop running anti-virus program to prevent zero day vulnerability. (Kaspersky Antivirus,.etc.)

Moreover, with my researches, I just divided Zero-day into two types:
- The hole is unknown.
- Fill in the hole but it's still not optimal.
I think the second kind of Zero-day is the most dangerous. Initially, if there is a flaw. For example, about 100 IT staffs are constantly day and night to fill that gap. Of course, when the gap is filled, the risk is prevented. Of course there are some people who check for this vulnerability but as in the example above, there will be only about 10 or fewer people who regularly test it. So the number of employees is reduced, if there are vulnerabilities attack immediately, those people can not keep up and the consequences can be unforeseen.



