In this article, we will see REST API in laravel. REST API is an application program interface that uses HTTP requests to GET, PUT, POST, and DELETE data. In this tutorial, I am going to perform a CRUD operation using REST API and you can learn how to create REST API with authentication using a passport in the laravel 7 application. here we will get data from API.
So, let's see REST API with crud operations and how to create REST API in laravel.
Laravel provides an easy way to create API. if you have authentication in your mobile app then you can easily do it using a passport. Laravel Passport provides a way to create auth token for validating users.
Type the following command in the terminal to create a new project.
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel REST_APINow, we are required to install the passport via the composer package manager. So, in your terminal run the below command:
composer require laravel/passportAfter installation of the package, We require to get default migration to create new passport tables in our database. So, run the below command.
php artisan migrateNow, We will install a passport using the passport:install command, it will create token keys for security.run below command:
php artisan passport:installNow, We have to configure on three place model, service provider, and auth config file.
1) HasApiTokens class of Passport has been added in the User model,
Add the below code in app/User.php
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\MustVerifyEmail;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
use Laravel\Passport\HasApiTokens;
class User extends Authenticatable implements MustVerifyEmail
{
use Notifiable,HasApiTokens;
/**
* The attributes that are mass assignable.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $fillable = [
'name', 'email', 'password',
];
/**
* The attributes that should be hidden for arrays.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $hidden = [
'password', 'remember_token',
];
/**
* The attributes that should be cast to native types.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $casts = [
'email_verified_at' => 'datetime',
];
}2) In AuthServiceProvider we have added "Passport::routes()"
Add below code app/Providers/AuthServiceProvider.php
<?php
namespace App\Providers;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Support\Providers\AuthServiceProvider as ServiceProvider;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Gate;
use Laravel\Passport\Passport;
class AuthServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
/**
* The policy mappings for the application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $policies = [
'App\Model' => 'App\Policies\ModelPolicy',
];
/**
* Register any authentication / authorization services.
*
* @return void
*/
public function boot()
{
$this->registerPolicies();
//
}
}3) We have added api auth configuration in auth.php.
In config/auth.php add the below code.
<?php
return [
'guards' => [
'web' => [
'driver' => 'session',
'provider' => 'users',
],
'api' => [
'driver' => 'passport',
'provider' => 'users',
],
],
];In this step, we will create migration of the Product table using php artisan command. So, run the below command in your terminal :
php artisan make:migration create_products_tableAfter running the above command, you will find migration in this path database/migrations. So, add the below code in your migration file to create the products table.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
class CreateProductsTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('products', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->text('detail');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('products');
}
}Now, run the below code in the terminal to create a migration.
php artisan migrateAnd add the below code in the app/Product.php file
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Product extends Model
{
protected $fillable = [
'name', 'detail'
];
}In step 5, we will create api routes. Laravel provides an api.php file for writing web services routes. So, let's add a route in the routes/api.php file.
<?php
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
Route::middleware('auth:api')->get('/user', function (Request $request) {
return $request->user();
});
Route::post('register', 'API\[email protected]');
Route::post('login', 'API\[email protected]');
Route::middleware('auth:api')->group( function () {
Route::resource('products', 'API\ProductController');
});Now, I have created BaseController, ProductController, and RegisterController in api folder.
app/Http/Controllers/API/BaseController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\API;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class BaseController extends Controller
{
public function sendResponse($result, $message)
{
$response = [
'success' => true,
'data' => $result,
'message' => $message,
];
return response()->json($response, 200);
}
public function sendError($error, $errorMessages = [], $code = 404)
{
$response = [
'success' => false,
'message' => $error,
];
if(!empty($errorMessages)){
$response['data'] = $errorMessages;
}
return response()->json($response, $code);
}
}app/Http/Controllers/API/ProductController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\API;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Product;
use Validator;
use App\Http\Controllers\API\BaseController as BaseController;
use App\Http\Resources\Product as ProductResource;
class ProductController extends BaseController
{
/**
* Display a listing of the resource.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function index()
{
$products = Product::all();
return $this->sendResponse(ProductResource::collection($products), 'Products Retrieved Successfully.');
}
/**
* Show the form for creating a new resource.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function create()
{
}
/**
* Store a newly created resource in storage.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function store(Request $request)
{
$input = $request->all();
$validator = Validator::make($input, [
'name' => 'required',
'detail' => 'required'
]);
if($validator->fails()){
return $this->sendError('Validation Error.', $validator->errors());
}
$product = Product::create($input);
return $this->sendResponse(new ProductResource($product), 'Product Created Successfully.');
}
/**
* Display the specified resource.
*
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function show($id)
{
$product = Product::find($id);
if (is_null($product)) {
return $this->sendError('Product not found.');
}
return $this->sendResponse(new ProductResource($product), 'Product Retrieved Successfully.');
}
/**
* Show the form for editing the specified resource.
*
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function edit($id)
{
//
}
/**
* Update the specified resource in storage.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function update(Request $request, $id)
{
$input = $request->all();
$validator = Validator::make($input, [
'name' => 'required',
'detail' => 'required'
]);
if($validator->fails()){
return $this->sendError('Validation Error.', $validator->errors());
}
$product = Product::find($id);
$product->name = $input['name'];
$product->detail = $input['detail'];
$product->save();
return $this->sendResponse(new ProductResource($product), 'Product Updated Successfully.');
}
/**
* Remove the specified resource from storage.
*
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function destroy($id)
{
$product = Product::find($id);
$product->delete();
return $this->sendResponse([], 'Product Deleted Successfully.');
}
}app/Http/Controllers/API/RegisterController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers\API;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Http\Controllers\API\BaseController as BaseController;
use App\User;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth;
use Validator;
class RegisterController extends BaseController
{
public function register(Request $request)
{
$validator = Validator::make($request->all(), [
'name' => 'required',
'email' => 'required|email',
'password' => 'required',
'c_password' => 'required|same:password',
]);
if($validator->fails()){
return $this->sendError('Validation Error.', $validator->errors());
}
$input = $request->all();
$input['password'] = bcrypt($input['password']);
$user = User::create($input);
$success['token'] = $user->createToken('MyApp')->accessToken;
$success['name'] = $user->name;
return $this->sendResponse($success, 'User register successfully.');
}
public function login(Request $request)
{
if(Auth::attempt(['email' => $request->email, 'password' => $request->password])){
$user = Auth::user();
$success['token'] = $user->createToken('MyApp')->accessToken;
$success['name'] = $user->name;
return $this->sendResponse($success, 'User login successfully.');
}
else{
return $this->sendError('Unauthorised.', ['error'=>'Unauthorised']);
}
}
}Now we have to create api resources, Laravel's resource classes allow us to expressively and easily transform our models and collections of our into JSON.
php artisan make:resource ProductNow, a New file is created on this app/Http/Resources/Product.php path.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Resources;
use Illuminate\Http\Resources\Json\JsonResource;
class Product extends JsonResource
{
/**
* Transform the resource into an array.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return array
*/
public function toArray($request)
{
return [
'id' => $this->id,
'name' => $this->name,
'detail' => $this->detail,
'created_at' => $this->created_at->format('d/m/Y'),
'updated_at' => $this->updated_at->format('d/m/Y'),
];
}
}After our adding all code we are ready to run full restful api in laravel.
Now, I have used POSTMAN API for testing purposes, Postman is a collaboration platform for API development. Postman's features simplify each step of building an API and streamline collaboration so you can create better APIs—faster.
Here I have added some screenshots with a description of the postman for your better understanding.
First of all, we need to register in postman to check our example.
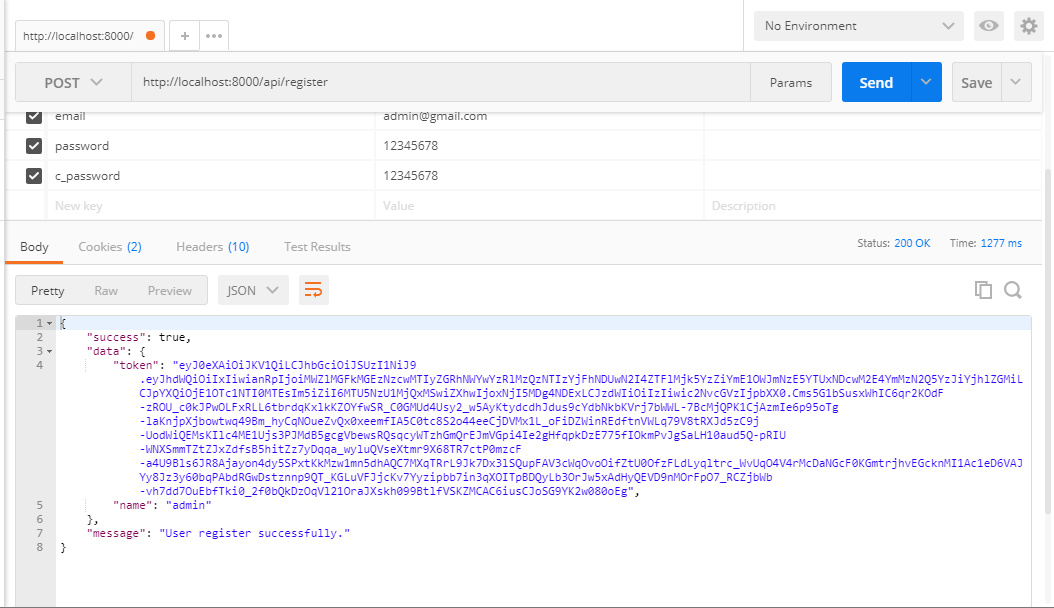






Finally, We are done with our code and it's your time to implement it in your project.
You might also like:
- Read Also: Laravel 8 User Role and Permission
- Read Also: How To Get Current User Location In Laravel
- Read Also: How to Send E-mail Using Queue in Laravel 7/8
- Read Also: How to Create Multi Language Website in Laravel