In this example we will see laravel 8 one to many relationship example. Also you can use one to many relationship in laravel 6 and laravel 7. A one to many relationship is used to define relationships where a single model is the parent to one or more child models. For one to many relationship use hasMany and belongsTo method in model for access each other model.
Also we will create migration with foreign key, retrieve records using model, insert new records, sync with a pivot table etc. So, let's see one to many relationship in laravel 6/7/8.
Now, We will create Articles and Comments table. Connect both table with each other and create one to many relationships with each other by using the laravel model. To define this relationship, we will place a comments functions on the Article model. The comments function should call the hasMany method and return its result.
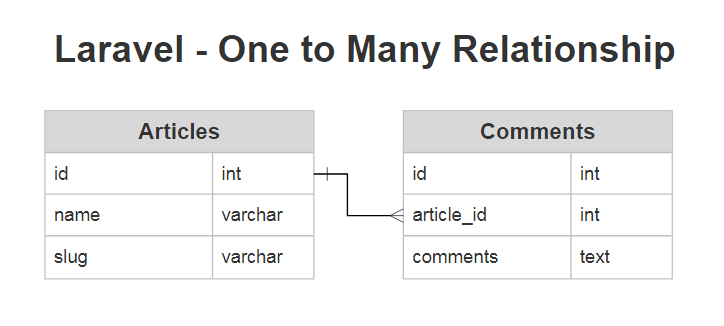
Now we have to create migration for articles and comments table. we will also add foreign key with articles table.
Create Migration of Articles Table
Schema::create('articles', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->string('slug');
$table->timestamps();
});Create Migration of Comments Table with Foreign Key
Schema::create('comments', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->integer('article_id')->unsigned();
$table->text('comments');
$table->timestamps();
$table->foreign('article_id')->references('id')->on('articles')->onDelete('cascade');
});In Article model we can create comments() function and add relation of Comment model using hasMany method.
Article Model :
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Article extends Model
{
/**
* Get the comments for the article.
*/
public function comments()
{
return $this->hasMany(Comment::class);
}
}Comment Model :
Now that we can access all of a article comments, let's define a relationship to allow a comment to access its parent article. To define the inverse of a hasMany relationship, define a relationship method on the child model which calls the belongsTo method.
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Comment extends Model
{
/**
* Get the article that owns the comment.
*/
public function article()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Post::class);
}
} In the example above, Eloquent will attempt to find a Article model that has an id which matches the article_id column on the Comment model. So, in this example, Eloquent will assume the Article model's foreign key on the comments table is article_id.
if the foreign key on the Comments model is not article_id, you may pass a custom key name as the second argument to the belongsTo method
/**
* Get the article that owns the comment.
*/
public function article()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Article::class, 'foreign_key');
}Once the relationship is defined, we may retrieve the related record using Eloquent's dynamic properties. So, here we can use Article model with comments function.
$comments = Article::find(5)->comments;
foreach ($comments as $comment) {
//
}$comment = Comment::find(7);
$article = $comment->article->name;$article = Article::find(1);
$comment = new Comment;
$comment->comments = "One To Many Exmaple";
$article->comments()->save($comment);In all relationship you can use condition onto query with model.
$comment = Article::find(1)->comments()
->where('name', 'websolutionstuff')
->first();You might also like :
- Read Also : Generate Dynamic Sitemap in Laravel
- Read Also : How To Create Dynamic Bar Chart In Laravel
- Read Also : Laravel 8 REST API With Passport Authentication
- Read Also : Drag and Drop File Upload Using Dropzone js in Laravel 8